Detailed Guide on Urinary Tract Infection (UTI): Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
What is a Urinary Tract Infections (UTI)?
How Urinary Tract Infection is Often Mistaken as Stomach Ache?
Referred Pain in UTI
Causes of UTI
- Sexual activity
- Using certain types of birth control
- Menopause, pregnancy and Underlying medical conditions that affect the urinary system.
Difference between Urinary Tract Infection and Bladder Infection
Urinary Tract Infection Symptoms
- Experiencing pain or burning while urinating
- The recurring urge to urinate despite the bladder being empty
- Having the impression that urinating has not completely emptied the bladder
- Urine that is cloudy, dark, or smells strongly
- Urine containing blood
- Lower back or stomach ache
- Chills or a fever (in more severe cases)
Urinary Tract Infection Causes
- Klebsiella
- Proteus
- Enterococcus
- Staphylococcus
- Streptococcus
- Pseudomonas
- Candida (yeast)
- Sexual activity
- Certain types of birth control (such as diaphragms or spermicidal agents)
- Menopause and hormonal changes
- Urinary tract abnormalities or blockages
- Poor hygiene
- Weakened immune system
- Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes or kidney stones
Body Factors:
Birth Control:
Abnormal Anatomy:
Immune System:
UTI Medicines:
- Trimethoprim / sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim, Septra)
- Nitrofurantoin (Macrodantin, Macrobid)
- Ciprofloxacin (Cipro)
- Levofloxacin (Levaquin)
- Amoxicillin (Amoxil)
- Ceftriaxone (Rocephin)
UTI Diagnosis and Urinary Tract Infection Treatment
- A physical exam.
- A discussion of symptoms.
- Laboratory tests such as a urinalysis and urine culture detect the presence of bacteria in the urine.

Home Remedies for a Urinary Tract Infections (UTI)
Drink plenty of water:
Cranberry juice:
Heat therapy:
Probiotics:
After Treatment:
UTI and Specific Populations:
Urinary Tract Infection Men:
- Although UTI is less prevalent in males than in women, it can still happen, particularly in older men with enlarged prostates.
- UTI symptoms in men are similar to those in women, including pain or burning during urination, frequent urination, and a strong urge to urinate.
- Antibiotics are frequently used to treat UTIs in men.
How Does a Woman Get a Urinary Tract Infection?
- Women's shorter urethras make it simpler for bacteria to enter the bladder, making them more susceptible to UTIs than men.
- The use of particular birth control methods, such as spermicides or diaphragms, sexual activity, menopause, and pregnancy, are all risk factors for UTI in women.
- By urinating after sexual activity, wiping from front to back after using the restroom, staying hydrated, and avoiding irritable feminine hygiene products, women can lower their risk of UTI.
- Antibiotics are frequently used to treat UTIs in women, though more extensive testing and care may be necessary if the condition is severe or recurs frequently.
- UTI symptoms female include a strong urge to urinate, frequent urine, and pain or burning during urination.
Urinary Tract Infections During Pregnancy:
- Preterm labor and low birth weight are two issues that can result from UTI, a frequent condition during pregnancy.
- Abnormalities of the urinary system, a history of recurrent UTIs, and diabetes are risk factors for UTIs during pregnancy.
- On their initial prenatal appointment and as needed for the remainder of their pregnancy, pregnant women should be checked for UTI.
- Antibiotics that are safe for the growing fetus are used to treat UTI during pregnancy, and it's crucial to get the condition under control right once to avoid complications. Staying hydrated and using proper hygiene practices might help women lower their risk of UTI during pregnancy.
Chronic UTIs:
What are Chronic UTIs?
Causes of Chronic UTIs:
Treatment Options for Chronic UTIs:
UTI Prevention:
Risk Factors for UTI
Female Anatomy
Sexual Activity
Menopause
Urinary Catheterization
Anomalies of the Urinary Tract
Immune System Issues
Diabetes
Dehydration
Ways to Prevent Urinary Tract Infections
- Cleaning the genital area before and after sexual activity, wiping from front to back after using the restroom, and avoiding using potent or strongly scented soaps, douches, and powders can all help prevent UTIs.
- Urination can help prevent bacteria from forming in the urinary system if done completely, frequently, and without holding it for too long.
- A lot of water and other liquids should be taken to aid in the flushing out of the germs in the urinary tract.
- Using cotton underwear and loose, breathable clothing can help minimize moisture accumulation, providing an environment for bacterial growth.
- Birth control: Prevent UTIs by using a birth control method like condoms or diaphragms that won't irritate the genital area.
- Supplements: Using probiotics or cranberry supplements may aid in preventing UTIs, while additional study is required to prove their efficacy.
- Sexual activity: You can help prevent UTIs by using condoms during sexual activity, peeing before and after sexual activity, and avoiding sexual engagement with someone with UTI symptoms.

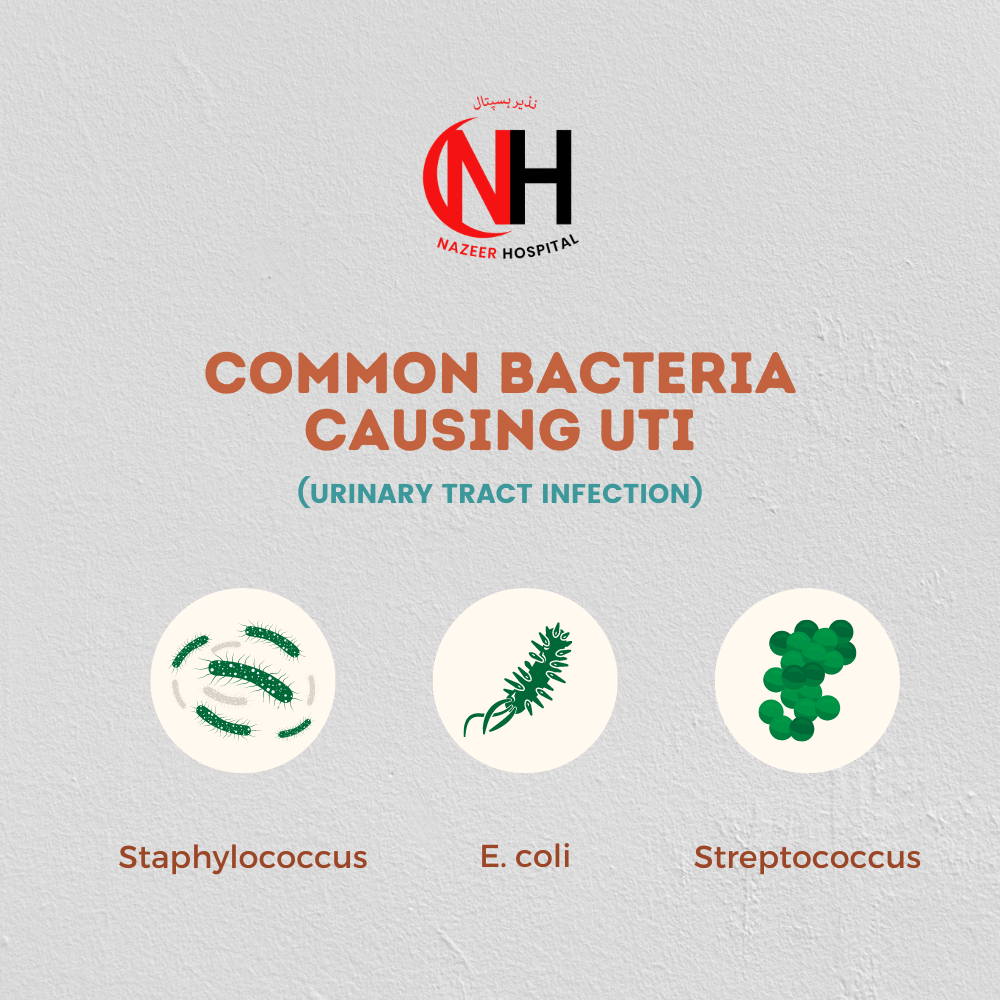
Common Bacteria Causing UTI:
- Escherichia coli (E. coli)
- Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Proteus mirabilis
- Enterococcus faecalis
- Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Types of UTI Bacteria
Lower UTI Bacteria
Upper UTI Bacteria
Conclusion:
Frequently Asked Questions
There are numerous causes of recurrent urinary tract infections (UTIs). The following are some frequent causes of UTIs that can raise risk:
- Female anatomy: Compared to men, women have shorter urethras, making it simpler for bacteria to enter the bladder and cause an infection.
- Sexual activity: By introducing bacteria into the urethra, sexual activity increases the risk of UTIs.
- Abnormalities of the urinary tract’s structural makeup, such as kidney stones or an enlarged prostate, can facilitate the growth of bacteria and the development of infections.
- Immune system compromise: A compromised immune system might make it more difficult for the body to fight illnesses.
- Usage of specific birth control methods: Spermicides and diaphragms are two methods linked to an increased risk of UTIs.
Discussing your recurring UTI symptoms with a healthcare professional to identify the underlying reason and create a suitable treatment strategy is crucial.
DR. KAMRAN ULLAH

Being an enthusiastic and well-trained entry-level physician who seeks to provide high-quality health care to help maximize patients’ well-being and facility profitability. Very resourceful and compassionate familiar with diagnosis and treatment of a wide range of diseases and health concerns.
DR. KAMRAN graduated from Khyber Medical University Peshawar. He has working experience at Rehman Medical Institute Peshawar, Agha Khan Hospital Karachi, PIMS Hospital Islamabad, and Mega Medical Complex Rawalpindi.
He has vast knowledge and experience and skills in the medical field. He is a highly dedicated and devoted doctor. He has worked on different medical research and published different research articles.
He is also a social activist and runs different social welfare organisations for the last 7 years, serving humanity and the needy. His main expertise are in the management of critically ill patients, patient care, health care quality, and safety.
